Modern businesses rely on integrated technology solutions to manage daily operations, track performance, and deliver seamless customer service. A Point of Sale (POS) system plays a central role in enabling these outcomes by streamlining sales transactions, managing inventory, and providing actionable business insights. Whether you run a café, a clothing store, or a cloud kitchen, a point of sale system serves as the operational backbone. How exactly? Let’s understand in detail what is POS, how it works, and what benefits it brings to a business.
| Table of Contents: |
| What is POS? |
| What Is The Benefit of POS System? |
| How Does Point Of Sale Set Up Work? |
| Types Of POS Systems |
| Choosing the Right POS System |
| Bottomline |
What is POS?
POS full form ‘Point of Sale’ is the point where a customer pays for the goods or services. A POS system combines multiple hardware and software components that manage this transaction while also recording important data for your business.
The components of a POS system include:
1. Point of Sale Machine (Hardware):
This includes the POS terminal (desktop computer, laptop, or mobile device), barcode scanner, card reader, receipt printer, and sometimes a cash drawer.
2. POS Software:
The software side handles sales records, inventory levels, discounts, user access, reporting, and customer data. Most POS software today is cloud-based and can be accessed remotely.
What is the Benefit of POS System?
With the combination of a point of sale machine and POS software, businesses can-
- Track daily, weekly, or monthly sales reports, broken down by product or category.
- Update stock levels in real-time when a sale is made and receive alerts when items are running low, thereby reducing the chances of manual errors.
- Store customer information, track purchase history, and set up loyalty programs to enhance customer experience.
- Accept various modes of payment, including cards, UPI, wallets, and EMI options through the point of sale machine.
- Manage user permissions, monitor shift timings, and track employee performance.
- Analyse which products sell best, what times are busiest, and how different branches are performing.
How Does Point of Sale Setup Work?
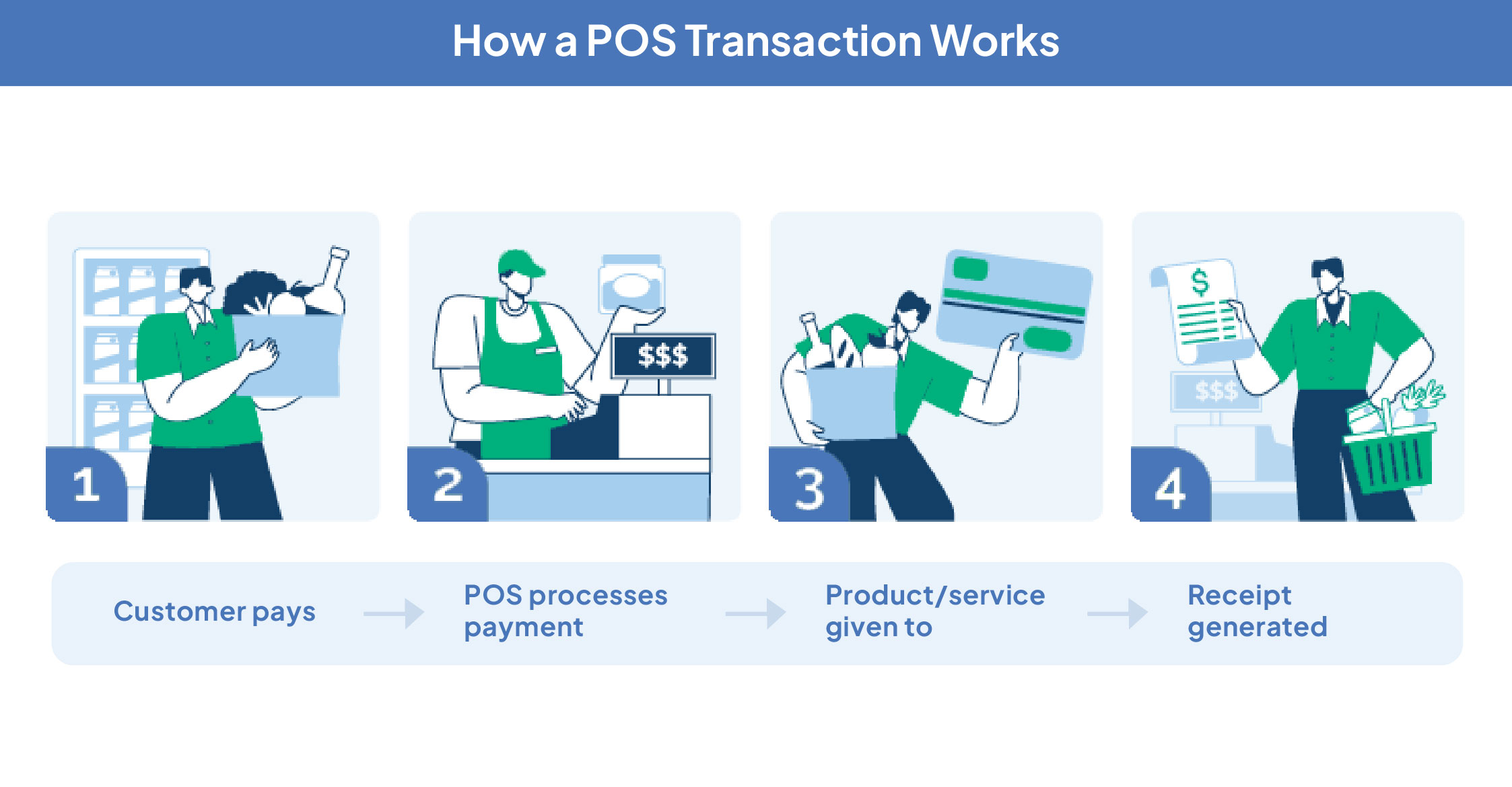
- The process begins when a customer brings selected items to the checkout counter and the cashier initiates a new transaction on the point of sale system.
- Each item is scanned using a barcode scanner for the system to retrieve product information from its database.
- It then calculates the total amount, applying any configured discounts, offers, or taxes.
- The customer chooses a payment method (cash, card, UPI, or mobile wallet) and the cashier completes the payment through the point of sale machine.
- The system then generates a receipt with transaction details and simultaneously updates the inventory by deducting the sold items from the current stock in real time.
- The transaction data is stored and used to generate sales reports, which provide insights into performance, popular products, and peak business hours.
Types of POS Systems:
Businesses today can choose from a wide range of Point of Sale (POS) systems depending on their size, operational model, and customer needs:
1. Traditional POS Systems (On-Premise POS)
These operate through on-site terminals and use dedicated hardware to store data locally. They are considered a reliable choice for brick-and-mortar stores and high-volume restaurants that prefer complete control over their data and require fast, offline transaction processing. However, they do require regular manual updates and maintenance.
2. Cloud-Based POS Systems:
These point of sale systems store transactional data on remote servers and enable real-time access to inventory, sales, and reports from any internet-connected device. They offer automatic backups, seamless software updates, and easy integration with e-commerce platforms and accounting tools, making them both scalable and low-maintenance.
3. Mobile POS (mPOS) Systems:
These systems run on smartphones or tablets and are perfect for businesses on the go, such as food trucks, vendor stalls, and small retail or service-based setups. They often use wireless card readers that accept contactless payments and provide real-time inventory tracking, making them affordable and easy to deploy without heavy hardware investments.
4. Self-Service Kiosk POS
Self-service kiosk systems let customers browse, order, and pay on their own. These are common in quick-service restaurants, cinemas, and retail self-checkout stations where they help reduce staffing requirements and speed up service.
5. Multichannel POS Systems
Multichannel POS systems sync sales and inventory data across physical stores, online shops, and marketplaces like Amazon or Shopify. For example, if a cosmetic store has 2,000 lipsticks in stock and sells 500 online and 1,200 offline, the system auto-updates the inventory to 300 in real time. This prevents overselling, ensures accurate stock levels, and unifies customer data, making it ideal for omnichannel retailers and subscription-based businesses.
6. Desktop POS Systems
Desktop POS systems are installed on a fixed terminal or computer. These systems usually suit small to medium-sized businesses that operate from a fixed location and prefer a traditional, stable setup for daily operations.
7. Tablet POS Systems
Tablet POS systems are portable, user-friendly solutions often used in cafes and restaurants for tableside ordering and payment. With sleek interfaces and easy mobility, they help improve customer interaction and significantly reduce wait times.
8. Open-Source POS Systems
Open-source point of sales systems offer the flexibility to customize features based on business needs. These are suitable for larger enterprises with technical resources, as they enable merchants to add advanced capabilities like barcode printing, custom reports, and tailored user interfaces. However, they require higher upfront costs and development expertise.
9. Terminal POS Systems
These systems use physical card-swiping devices to process transactions in retail and hospitality environments. These are simple systems often paired with receipt printing and SMS/email notifications, making them suitable for stores and restaurants that regularly handle card payments.
10. Specialized POS Systems
Industries like healthcare, salons, and auto repair may benefit from specialized POS solutions with niche-specific features. These systems include custom workflows, appointment scheduling, and billing tools that align with the unique requirements of their sectors.
11. Mobile Wallet & Contactless Payment POS
These POS systems are equipped to handle digital wallet transactions like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and contactless cards. They’re essential for businesses that want to offer fast, modern payment options to improve checkout speed and enhance customer satisfaction.
Choosing the Right POS System:
Not every business needs an advanced system with all the bells and whistles. When selecting your POS system, consider the following:
- Type of Business: A retail store may need barcode support, while a restaurant may need a table management feature. So, understand your industry, business size, and transaction volume to identify the right features and functionality required.
- Hardware Compatibility: Check whether the POS software works well with your current tools, like inventory, CRM, and accounting software.
- Customer Support: A good support team can make implementation and troubleshooting easier. So, always check for reliable, 24/7 customer support via phone, email, or chat.
- Trial or Demo: Use free trials or demos to test usability, fit, and performance in your real business environment before finalizing.
- Budget: Define a realistic budget, including setup and recurring costs, to narrow down suitable options.
Bottomline:
As businesses evolve, so do their operational needs, and the role of POS systems has expanded to match. Understanding what a POS system is and how it aligns with your workflows can help you make an informed and future-ready choice. In today’s dynamic business landscape, investing in the right point of sale setup isn’t just a convenience; it’s a strategic step toward streamlined operations and sustained growth.



