As a business owner, you may accept payments from customers and other parties through various modes, including UPI (Unified Payments Interface), digital wallets, net banking, bank transfers, credit and debit cards, among others. While you may offer different payment options to accommodate the customer’s convenience and preferences, you may also be vulnerable to payment fraud. This is where payment Tokenization plays an important role in preventing fraud and providing an exceptional customer experience.
If you are unsure what Tokenization is, how it works, or why it is important for businesses, then this guide is for you. We explore the fundamentals of Tokenization and its unique benefits for different types of businesses.
Table of Contents
What is payment Tokenization?
Payment Tokenization, also known as credit card Tokenization, is essentially a security technique that replaces sensitive payment-related information, such as credit card numbers and CVV (card verification value) codes, with a random set of characters called a ‘token’.
This process helps keep payment data safe and secure while transactions are processed, as sensitive data is not stored or saved. If anyone tries to steal or access the token details, they won’t be able to use them to make fraudulent purchases, as they do not contain the actual payment details.
By using tokens and implementing a card Tokenization system, businesses can offer a secure and seamless payment experience for their customers while reducing the risk of data breaches and fraud.
Working of Tokenization in payments
Tokenization of debit card payments and other payment modes transforms sensitive card data into a non-sensitive equivalent that can be stored and safely transmitted without exposing the actual payment-related data to potential threats or fraud. In the context of payment processing, the working of Tokenization is as follows.
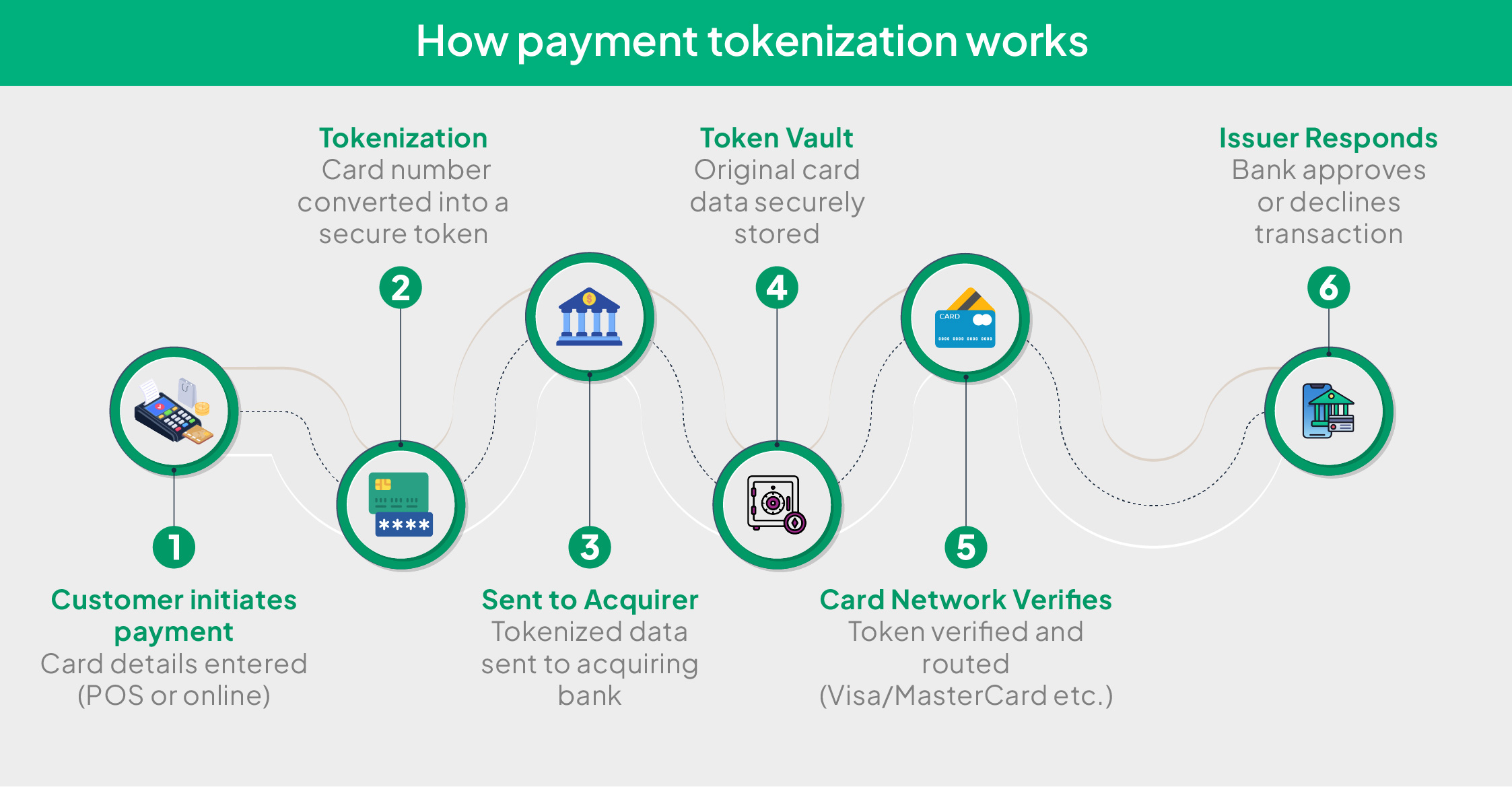
Step 1 – Customer input
Let us assume you are the business owner. A customer walks into your store, makes a purchase and initiates the payment. The customer wishes to pay with this credit card and swipes the card at the point-of-sale (POS) machine. Alternatively, let’s assume the customer makes an online purchase from your website and enters their credit card information at the checkout page.
Step 2 – Tokenization
After the customer enters their credit card details on the website or swipes their card, the card details are passed to the Tokenization service through a payment process or a tokenization-enabled software or hardware system. It then generates a token, which is basically 16 random characters, replacing the original card number and sends it to the token vault.
There are different ways for creating tokens, like reversible cryptographic functions, index functions, non-reversible functions, etc.
Step 3 – Transferring the data to the acquirer
The tokenized transaction details are then forwarded to the acquirer, which handles the payment request on behalf of the business enterprise.
Step 4 – Storing the token in the token vault
A centralised server, which is known as the token vault, securely stores the original sensitive card-related information and maps it to the corresponding token that is generated. The system then returns the 16-character token to the POS machine or the business website to replace the card details in the system.
Step 4 – Verification
The acquirer sends the tokenized information to the card network (VISA, MasterCard, American Express, etc.), which then verifies the token and ensures that the transaction is routed safely.
Step 5 – Transaction approval or rejection
The issuer, i.e., the bank issuing the card to the customer, validates the transaction by checking the balance in the customer’s bank account and sends an approval or rejection message.
Different formats of Tokenization in payments
There are different formats of payment Tokenization, and the classification is done based on the token characteristics and their functions.
- Non-format preserving tokens
In non-format-preserving tokens, the tokens take an entirely different format, and they do not resemble the original credit card number. The tokens typically include a random set of alphanumeric characters.
For example, if your card number is 1468 2356 7869 8901
The non-format preserving token could be 24c82e19-79c4-104x-0l35-3798s45y1882
- Format-preserving tokens
In format-preserving tokens, as the name itself suggests, the tokens maintain the same format as the original card information. However, the values of the are changed randomly.
For example, if your card number is 1468 2356 7869 8901
The format-preserving token could be 7690 2498 1121 2500
- Partial replacement tokens
A partial replacement token is a type of format-preserving token in which some of the values are left unchanged. This is also commonly referred to as selective masking, and it is a very common practice for payment tokens.
For example, if your card number is 1468 2356 7869 8901
The partial preserving token could be 1468 2480 4892 8901 or 1468 AUH# BID& 8901
Benefits of payment Tokenization for various businesses
Now that you know how payment Tokenization worksand its different formats, let us explore the importance of payment Tokenization for various types of businesses.
Payment Tokenization offers a wide range of benefits for different types of businesses that accept payments via debit or credit card and other digital payment modes.
- Improved security
Tokenization in payments plays an important role in reducing the risk of data breach and fraud as it replaces the sensitive card information with a non-sensitive token. This ensures that the actual payment data is protected from fraudsters and scammers during the transaction, minimising the risk of unauthorised access or misuse of the data.
- Legal compliance
By minimising the storage and processing of sensitive card-related payment information, Tokenization enables business organisations to be compliant with their industry standards like PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards). Being PCI DSS compliant is not only important for businesses from a legal point of view and to avoid paying penalties, but also to win their customers’ trust and loyalty.
- Enhanced customer experience
By reducing the risk of payment fraud and ensuring customers that their sensitive information is safe and protected, you can create a smoother checkout experience for them, while also earning their trust in your business. A simple payment experience, including the reuse of tokens for returning customers, can help increase customer loyalty, drive repeat purchases, and boost sales.
- Streamline the account management process
If you own any subscription-based business, then you may have to handle frequent changes in the customer’s preferred payment mode, or changes in their subscription plans; they may upgrade or downgrade their plan. Additionally, you may also have to handle the subscription cancellations.
By implementing payment Tokenization in the checkout process, you can streamline the account management process by allowing the same tokens to be used for different transactions and accommodate changes without worrying about leaving the customer’s sensitive data exposed to fraudsters.
- Point of sale security
Although POS (point of sale) transactions, in which the customer presents a physical card to be swiped on the POS machine, are considered more secure, fraudsters may still attempt to steal this data. This is where Tokenization in payment helps; it enhances security by ensuring that sensitive data is not stored within the POS system, thus restricting unauthorised access and preventing data breaches.
- Mobile payments solutions
Today, just like online retail outlets and e-commerce platforms, most brick-and-mortar stores also offer mobile payment options to their customers. For such a business, Tokenization is crucial to ensure that all transactions are processed and completed efficiently and securely.
The best thing about Tokenization is that it also works with digital wallets and contactless payment modes, providing an additional layer of security while supporting new payment technologies.
- Reduced liability
By implementing Tokenization in payment systems, business organisations can reduce the risk of sensitive payment data breaches or unauthorised access. Thus, it effectively limits the business’s liability in the event of a data breach. Additionally, it helps businesses protect themselves from reputational damage and potentially significant financial loss.
- Increase payment efficiency
This is another significant benefit that businesses can enjoy by implementing Tokenization in the payment process. It helps business owners keep customers’ tokens instead of the actual sensitive data in their records, which streamlines the entire payment process.
Instead of manually entering the payment information every time the customers initiate a transaction, they can set up a recurring or one-click payment and complete the transaction quickly and securely.
- Cost control
Tokenization significantly simplifies payment security, and the entire system is PCI DSS compliant. Therefore, business owners need not worry about not adhering to industry standards or failing to meet legal obligations. Additionally, they do not need to invest in external security measures to safeguard the customer’s sensitive data and ensure the transaction process is secure.
Additionally, by securing payments, Tokenization helps reduce the risk of data breaches and the associated costs, such as legal fees, loss of business, and fines.
Tokenization in India – RBI Guidelines
The RBI has allowed the Tokenization of debit card, credit card, and prepaid card transactions in India, primarily with the aim of promoting digital payments and protecting customer data. In that regard, the RBI has also issued certain guidelines for Tokenization services, including:
1. Tokenization is not mandatory, but a business organization can implement it voluntarily in their payment process, requiring explicit consent through AFA (Additional Factor of Authentication).
2. Card companies have the authority to decline tokenized payment requests for security reasons.
3. As of October 1, 2022, all online merchants and business owners who have implemented Tokenization in their payment processes are prohibited from saving customers’ card details.
Conclusion
Tokenization in payments is a boon for both customers and business owners. It helps businesses improve their data security and eliminates the actual storage of card details in POS machines and internal systems. Also, it minimizes the impact of security breaches on the business.
For customers, Tokenization makes the entire payment process more convenient and secure, giving them peace of mind knowing that even in the event of fraud or theft of card details, hackers or miscreants will only acquire the tokens and not the actual sensitive data.
Offer seamless & secure payments with PayU and grow your business. Start today!



