In the times before the present startup culture took over in India, it took close to a decade for a business to reach the unicorn stage. Take, for instance, fantasy sports giant Dream11 and Pune-based software company Druva, both of which took 11 years to hit the billion-dollar mark. Interestingly, the time it takes to get to the unicorn stage has decreased drastically in the last five to six years. Food aggregators such as Swiggy and Zomato have entirely changed the face of the startup ecosystem in India by becoming unicorns in record time. Zomato’s successful IPO on the stock exchanges speaks volumes of the potential these startups have gathered.
Over the last ten years, India’s startup ecosystem has gained significant traction. The country is witnessing unicorns emerging frequently. Thanks to supportive government policies and a younger population ready to challenge the normal, many startup entrepreneurs are eyeing the bigger and stronger stakes in the market.
Is there a secret recipe to their success apart from hard work and hustle? Not many. But a close look at the different stages could help derive unique strategies. Continue reading to learn more about the stages of a startup.
Different Stages of Startups
The following are the different stages of a startup:
- Early stage
This stage is the beginning of the startup’s journey and can be further subdivided into:
Ideation: This stage is one of the most important in the entire startup journey because it is the one that decides how long the startup journey will go. In the ideation stage, founders brainstorm and zero in on ideas that make business sense. The startup ecosystem in India has several incubators that can greatly help the founders at this stage. Some of the most famous incubators in India include Atal Incubation Centres (AICs) and K-Tech Innovation Hubs.
Pre-seed: At this stage, the founders have already identified the idea and have the structure of the startup ready. Moreover, they also have a prototype ready with a business plan in place. The business plan has details of the financial requirements and capabilities of the idea and company. It also includes the go-to-market strategy and prospects as per the current findings of the market in which the startup would fall. This sharp and to-the-point business plan would enable the startup to present its case to investors and draw their interest.
Seed: At this stage, the startup has a few paying clients, and the growth trajectory is on a positive curve. During the seed stage, the startup looks at raising funds to help it launch the first level of marketing strategy and build products and a team.
Typically, early-stage investments arrive from friends and family, government grants, and angel investors. The investment size at this stage depends on the kind of business plan a startup has to offer.
- Growth stage
In this, the startup goes through various series of startup funding stages:
Series A: The Series A funding is used to optimise the startup’s technology, team, research and development efforts. The startup needs to have a consistent revenue generation track record of getting this funding.
Series B: Since the startup has a sustainable revenue source at this stage, the finances fall clearly into their respective buckets. The Series B funding is required to improve processes, expand teams with specialised employees, and undertake deep market study and analysis to enhance offers.
- Expansion stage
With the startup standing on firm ground, it can now look at spreading its wings. In this stage, the startups look at fundraising to tap newer opportunities and expand their reach to newer markets or globally.
- Series C
By this stage, the startups now have a significant geographical presence and are eyeing expanding their overseas reach. They are looking at venturing into newer markets with improved products and services. Series C funding typically comes from hedge funds, investment banks, and private equity firms.
- Series D, E
At these stages, fundraising is focused on rectifying mistakes and acquiring smaller or similar interest startups that might pose a threat shortly. The funds also tap newer markets through a multi-layered marketing strategy.
- IPO/Exit Stage
It is the stage of full glory as the startups are ready to go public. The startups float Initial Public Offerings (IPOs), which include offering a particular amount of shares to the public at an amount. The proceeds of the IPO are used to expand the startup’s business strategy further and prepare it for the next level of growth. It is also the stage that provides exit opportunities to investors. This is the next critical stage in the journey of startups after ideation, as it involves a lot of financial documentation and asset audits to become a unicorn.
Every stage of the startup is unique in its own way. With its own set of challenges and opportunities, each stage provides a good opportunity for startups to learn, improve, and grow. The Indian startup ecosystem has been transforming fast, with more ideas hitting the market and multi-niche success.
Various Stages of Venture Capital
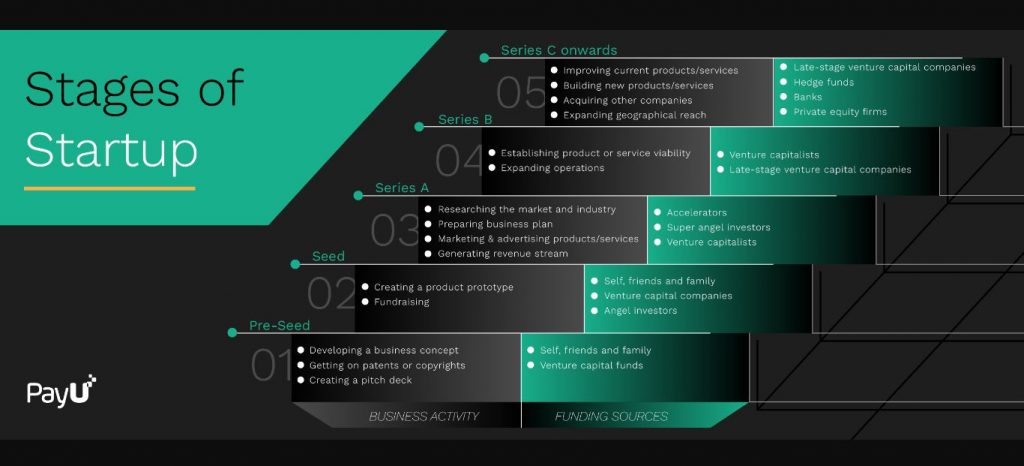
Source: Inc42
FAQs
A startup is an entrepreneurial project that is undertaken with one’s own investment or with the help of third parties to realise the successful monetisation of one’s idea.
Yes, each stage is important in the startup journey, irrespective of the size or industry it falls into. These stages nurture the startups and they emerge successful.
It is important to develop a sustainable startup ecosystem supported by incubators, policymakers, and venture capitalists to reduce the time taken by each stage. The Indian ecosystem is evolving with a significant focus on reducing the time taken by startups at each stage.





